How do government policies impact foreign exchange markets?
Updated on 4/24/2024 Jacob Reed
In the article below, we are going to explore the impact of government policies on the foreign exchange markets. You have already learned about the domestic impacts that occur when the government implements trade policies, monetary policies, or fiscal policies. Below, we will look at the effects of those same policies on exchange rates.

How Do Trade Restrictions Impact Exchange Rates?
As you may have learned in Microeconomics, trade restrictions such as tariffs and quotas reduce the amount of imports a country will buy from other countries. If the United States puts a tariff on goods imported from India, that will raise the price of Indian goods in the United States. US citizens will purchase fewer Indian goods. That means consumers will supply fewer US Dollars in the foreign exchange markets and Demand fewer Indian Rupees. As a result, the US Dollar will appreciate (exchange rate increases) and the Indian Rupee will depreciate (exchange rate decreases).
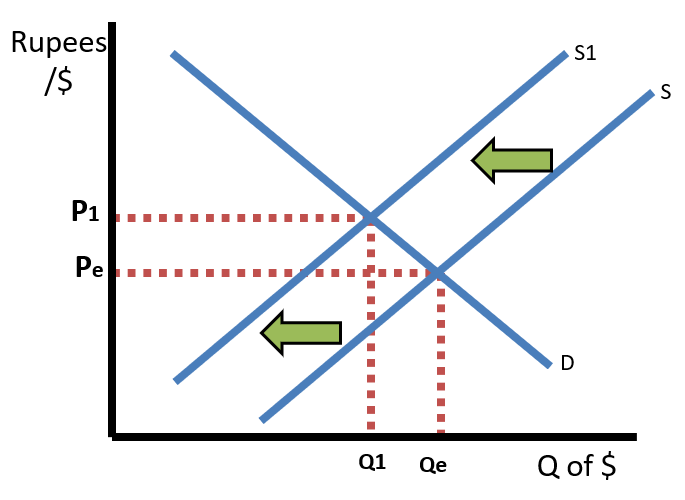

Likewise, if the United States removed a tariff on Indian goods, that would decrease the price of those goods. US consumers would then buy more imports from India. That means US consumers will supply more US Dollars and demand more Indian Rupees, causing the US Dollar to depreciate and the Indian Rupee to appreciate.

How Do Changes In Real Income (Real GDP) Impact Exchange Rates?
Whenever you see changes in Real Income on the AS/AD model, that change in income will impact the foreign exchange markets. Monetary and fiscal policy change real income, so they also cause changes in the exchange rate. Essentially when a country has more income, it purchases more goods, including imported goods. The change in imports impacts foreign exchange markets.
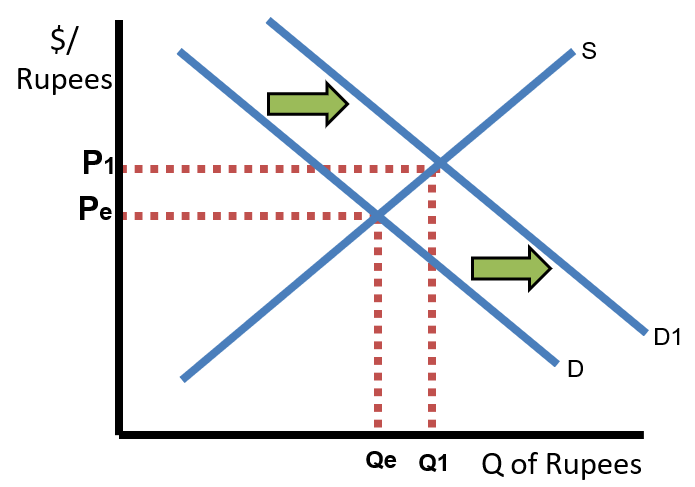
Expansionary fiscal and expansionary monetary policy both cause a rightward shift of the AD curve, which increases real income (rGDP on the x-axis). When a country has more real income, it purchases more goods and services, including goods and services from other countries. So, if US real income increases, US consumers will import more goods from India. That increases the supply of US Dollars and increases the demand for Indian Rupees, causing the US Dollar to depreciate and the Indian Rupee to appreciate.


Contractionary fiscal and monetary policy, on the other hand, both cause a leftward shift of the AD curve, which decreases real income and decreases imports. So, if US real income decreases, consumers will buy less of everything, including goods made in India. That decreases the supply of US Dollars and decreases the demand for Indian Rupees, causing the US Dollar to appreciate and the Indian Rupee to depreciate.


How Do Changes In The Price Level Impact Exchange Rates?
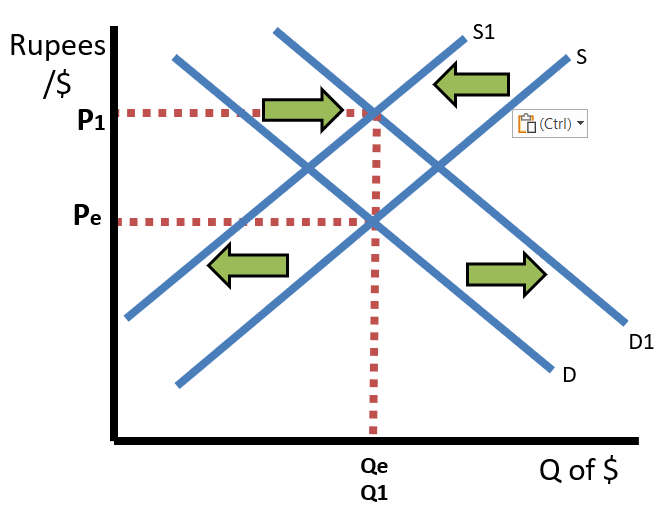
Fiscal and Monetary policy also change the price level in a country and those changes impact the relative prices of imports and exports along with exchange rates. If the United States has expansionary monetary policy and/or expansionary fiscal policy, there will be a rightward shift of the AD curve which cause the United States price level to increase. This would make US made goods more expensive and foreign goods (like those in India) relatively cheaper for US consumers. That means US imports will increase and US exports will decrease. In the market for the US Dollar, we will see an increase in supply (from the increased imports) and decrease in demand (from the decreased exports), causing the US Dollar to depreciate. In the market for the Indian Rupee, we will see a decrease in supply and an increase in demand, causing the Indian Rupee to appreciate.


If the United States has contractionary monetary and/or fiscal policy, there will be a leftward shift of the AD curve and a decrease in the price level. As a result, US goods would be cheaper and foreign made goods (like those from India) will be relatively more expensive for US consumers. US Imports will decrese and US exports will increase. In the US Dollar market, the supply will decrease, and the demand will increase, causing the US Dollar to appreciate. In the Indian Rupee market, the supply will increase, and the demand will decrease; causing the Indian Rupee to depreciate.

How Do Changes In Interest Rates Impact Foreign Exchange Markets?
Since changes in interest rates change financial capital inflows and outflows, which also change the supply and demand within foreign exchange markets. Since fiscal policy changes interest rates in the loanable funds market and monetary policy changes interest rates in the money market and/or reserves market, these policies can also impact exchange rates through interest rates.
If the US has expansionary monetary policy and/or contractionary fiscal policy, US interest rates will fall. Those lower interest rates cause a financial capital outflow. Foreign investors will seek higher interest rates elsewhere. That will cause decrease in demand and increase in supply of the US Dollar, causing the US Dollar to depreciate. If interest rates in India didn’t change, financial capital will flow into India because of the relatively higher interest rates. That will cause an increase in demand and decrease in supply of the Indian Rupee, causing it to appreciate.


If, on the other hand, the US has contractionary monetary policy and/or expansionary fiscal policy, US interest rates will rise. Investors around the world will seek those higher interest rates, so the US will see a financial capital inflow. That inflow will cause an increase in demand and decrease in supply of the US Dollar. The US Dollar will appreciate as a result. India will see a financial capital outflow because of interest rates increasing in the US. That will cause a decrease in the demand and increase in supply of the Indian Rupee. The Indian Rupee will depreciate as a result.


Note: You could notice that some policy actions have conflicting impacts on the foreign exchange markets depending on whether you focus on changes in the price level, real income, or interest rates. Read questions carefully, there will usually be a indication on what variable(s) you should focus on.
