How Do Exchange Rates Impact Net Exports?
3/27/2024 Jacob Reed
In this article we are going to explore the impact of foreign exchange rates on net exports. Changes in exchange rates cause the relative prices of exports and imports to change, which in turn changes net exports and shifts aggregate demand. Keep reading to find out how.
Currency Appreciation
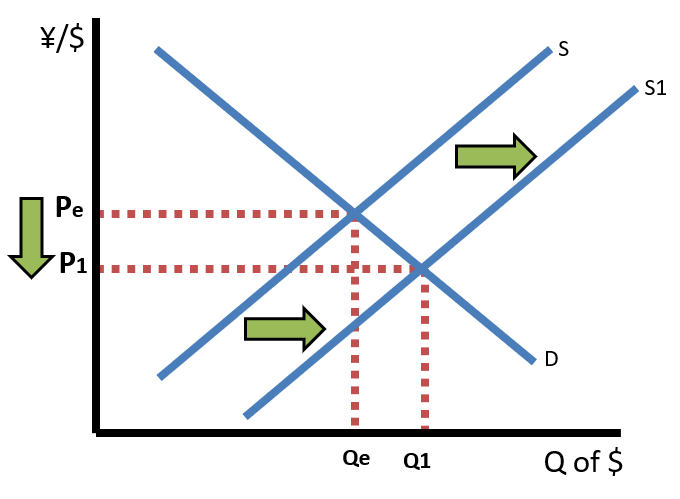
Suppose we have two radios, one made in Japan and the other made in the United States. The radio made in Japan sells for 3,000 yen, while the radio made in the United States sells for 25 US dollars. If the exchange rate is for the US dollar is 150 Japanese yen to 1 US dollar, the radio made in Japan will cost $20 in the US and the radio made in the US will cost ¥3,750 in Japan.
If the US dollar appreciates and the exchange rate for the dollar rises to 200 Japanese yen to 1 US dollar, that will change the relative prices of both radios. While price in Yen for the Japanese radio remains ¥3,000, it will now sell for $15 (¥3,000/200¥/$) in the US. The Japanese radio just got $5 cheaper for US consumers. Also, while the price in Dollars for the US radio remains $25 it will now sell for ¥5,000 ($25 x 200¥/$) in Japan. The US radio is now ¥1,250 more expensive for Japanese consumers.
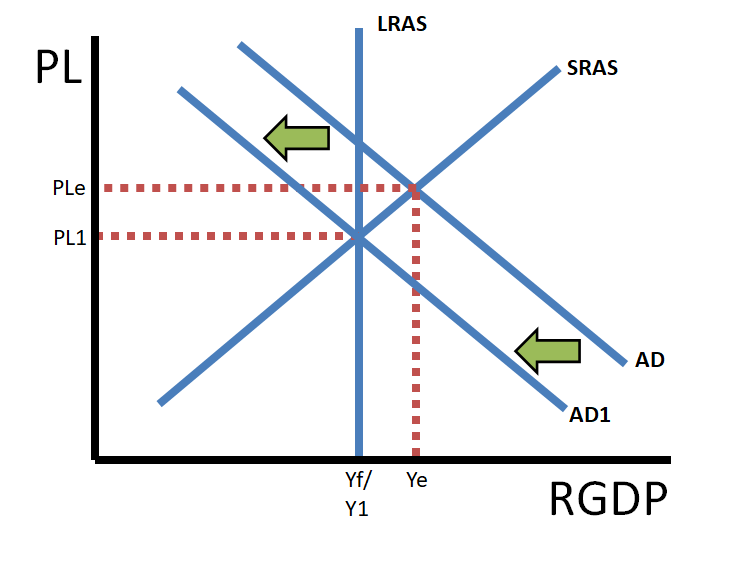
So, when a currency appreciates, imports get cheaper for domestic consumers and exports get more expensive for foreign consumers. As a result, imports increase and exports decrease which means net exports decrease. The decrease in net exports will cause a leftward shift of the AD curve, decreasing the price level and real output.
Currency Depreciation
Let’s use those same radios above as another example. This time, the US dollar depreciates, and the exchange rate falls to 100 Japanese yen to 1 US dollar. The lower exchange rate means that the Japanese radio now costs $30 (¥3,000/100¥/$) in the US. The Japanese radio is now more expensive for US consumers. Also, while the US radio still sells for $25, it is now ¥2,500 ($25 x 100¥/$).
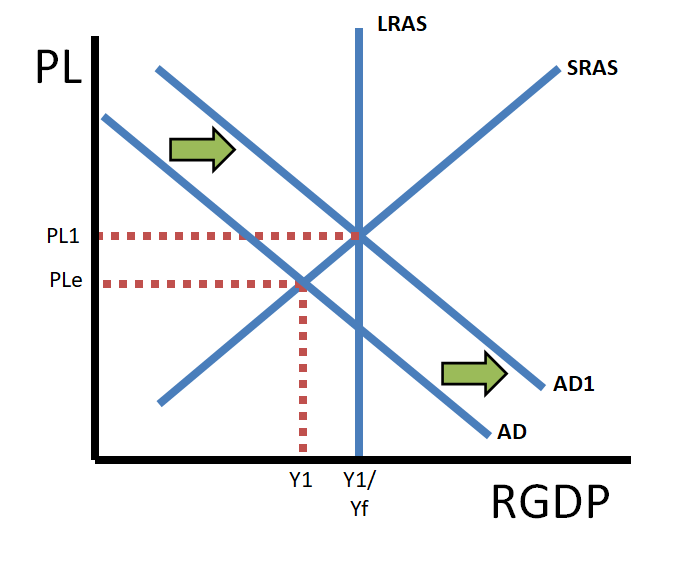
So, when a currency depreciates, imports get more expensive for domestic consumers and exports get cheaper for foreign consumers. As a result, imports decrease, and exports increase which means net exports increase. The increase in net exports will cause a rightward shift of the AD curve, increasing the price level and real output.
Impact on the Balance of Payments
In the balance of payments imports are recorded as a debit and exports are a credit. That means when a currency appreciates, the decrease in net exports will cause the Current Account balance to decrease. Since the Capital and Financial Account always balances out the Current Account, the decrease in the current account balance will cause an increase in the Capital and Financial Account balance.
When a currency depreciates, on the other hand, net exports will increase, causing an increase in the Current Account balance. The increase in the Current Account necessarily means a decrease in the Capital and Financial Account.
